The following types of layers are available in FireAlpaca / FireAlpaca SE.
Color Layer
Color layer consists of pixels with four elements: [R (red)], [G (green)], [B (blue)], and [A (alpha, opacity)]. Each element of [R], [G], [B], and [A] can have 256 possible values (=8 bits) from [0] to [255], color and opacity are determined by the combination of these values. Since it consists of four elements with 8-bit values, it is also called [32bit layer (= 8bit × 4)].
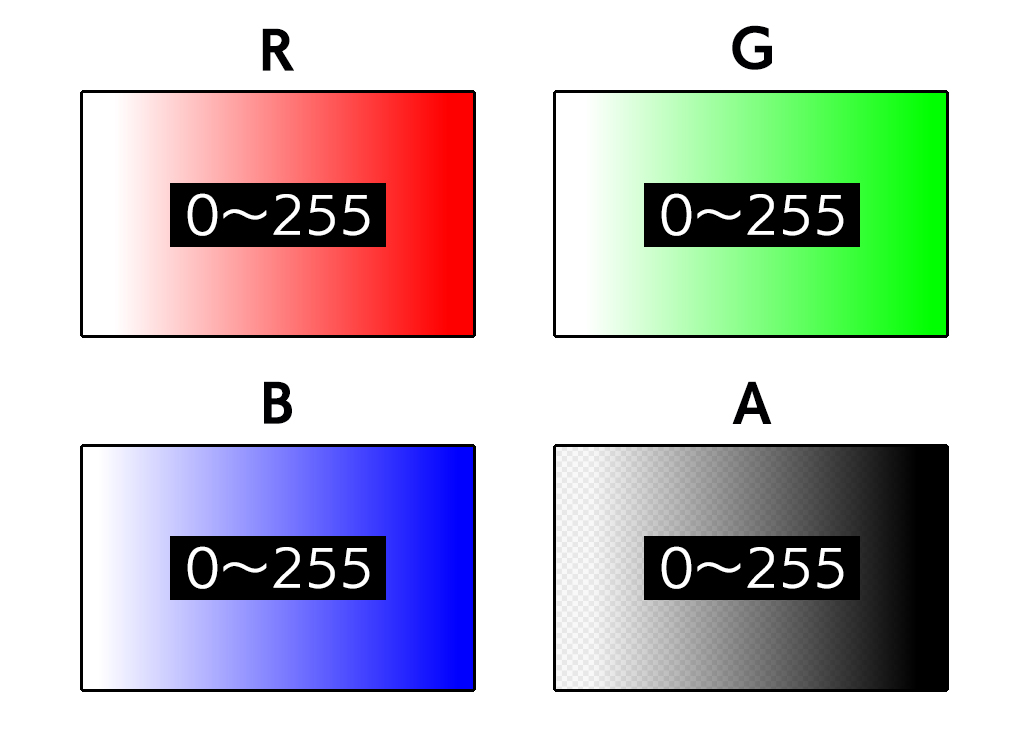
Example of color layer illustration
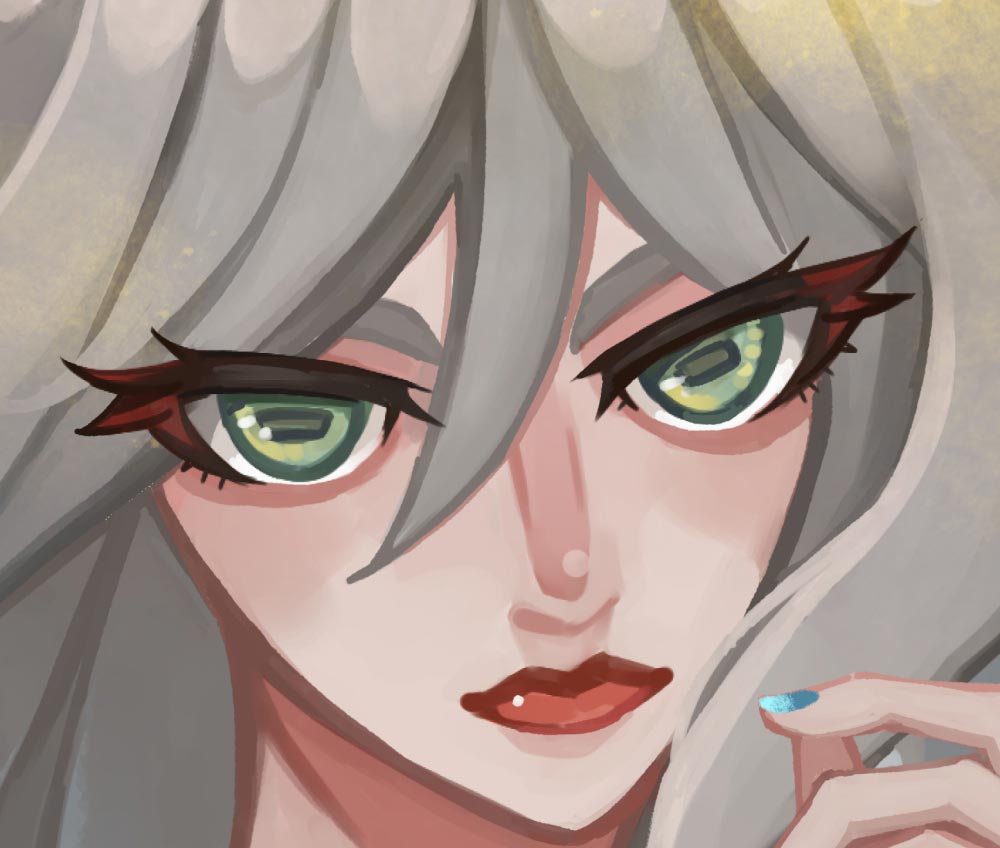

8bit Layer
8bit layer is a layer lacking of [R], [G], or [B] elements, but only with an [A (alpha, opacity)] element. The [A] element can have 256 possible values (=8 bits) from [0] to [255]. Since there are no [R], [G], or [B] elements, the amount of data can be reduced to 1/4 of that of color layer (32bit layer).
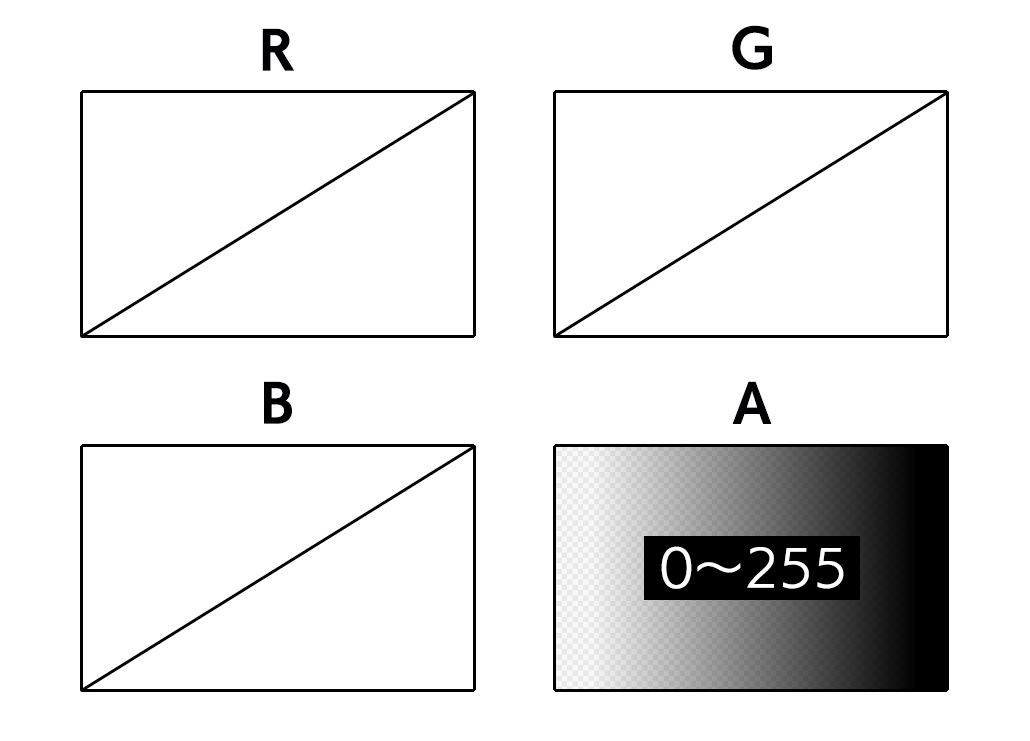
Although the pixels of an 8bit layer itself do not have [R], [G], and [B] elements, only one color can be set on each layer.
Example of 8bit layer illustration
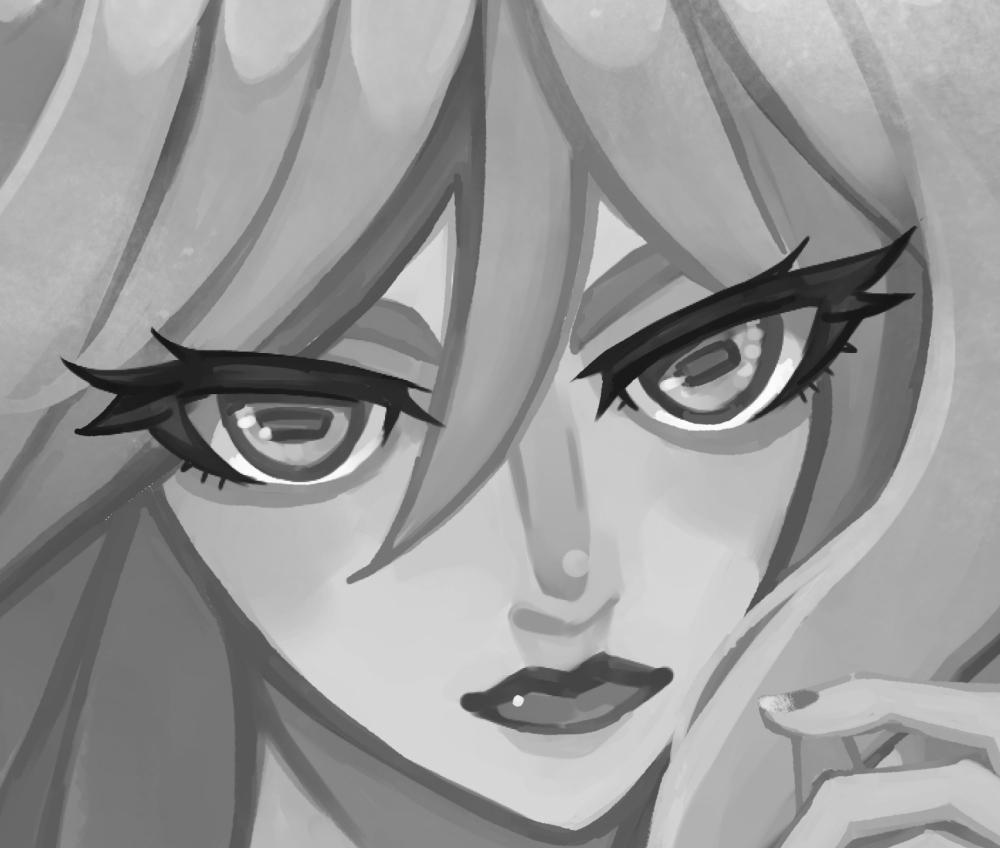

1bit Layer
1bit layer is like 8bit layer, lacking [R], [G], and [B] elements, but only with [A (alpha, opacity) element. The difference from 8bit layer is that each element of [A] can have only two possible values [0] and [1] (=1bit). This allows for even lower data volume than that of 8bit layer.
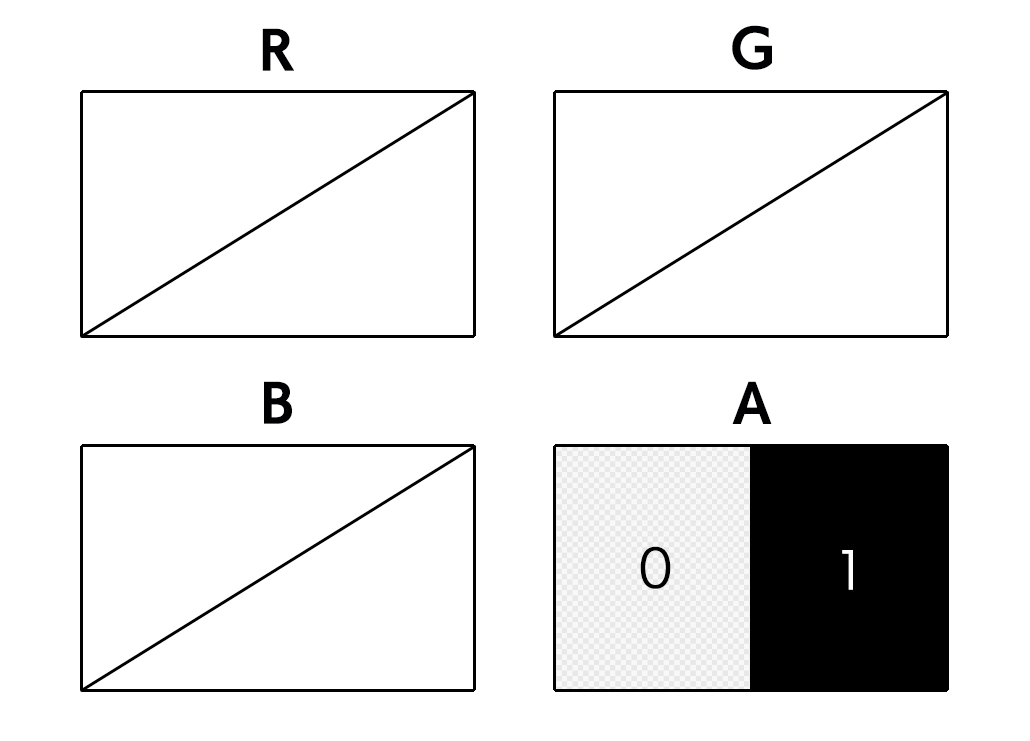
Anti-aliasing is not applied to images drawn on 1bit layer. It is used when creating [Monochrome (1bpp)] images such as comic book manuscripts for printing.
Like 8bit layer, only one color can be set on each layer.
Example of 1bit layer illustration

Mask Layer
Mask layer is always added in a clipped form. You can partially hide the clipped layer while drawing on a mask layer. This creates an effect similar to that of layer mask, only the appearance of the layer can be changed without altering the original layer image.
Anti-aliasing can be applied because mask layer consists of pixels with an [A (alpha, opacity)] element that can have 256 possible values (=8bit) from [0] to [255]. If you draw with a color other than black (opacity 0), the clipped layer will be hidden with an opacity corresponding to the [A] value when converted to grayscale.
Stencil Layer
Stencil layer is always added in a clipped form. Drawing on a stencil layer partially reveals the layer to be clipped. Only the appearance of the layer can be changed without altering the original layer image.
Anti-aliasing can be applied because stencil layer consists of pixels with an [A (alpha, opacity)] element that can have 256 possible values (=8bit) from [0] to [255]. If you draw in a color other than black (opacity 0), the clipped layer will be shown with an opacity corresponding to the value of [A] when converted to grayscale.
Text layer
Text layer contains text data made by text tool.
For instructions about how to edit texts, please refer to “Text Tool” on this page.
To text layer you cannot draw with brush tool, erase with eraser tool, transform, nor apply filters. If you want to do these actions, you need to convert text layer to pixels by [Copy] > [Paste] or [Convert Text Layer to Image Layer] (choose text layer and right-click). Once a text layer has been converted to pixels, you can no more edit it with text tool.
3D Perspective Layer
This layer is for editing 3D objects of 3D perspective snap. For details on how to use it, please refer to “3D Perspective Snap” on this page.
Layer Folder
You can put together multiple layers into one folder. Selecting a layer folder, you can move, transform and change [Opacity] and [Blending] settings of all layers contained within it. Only for layer folder, you can set [Pass Through] for [Blending].




